ASNM-TUN Dataset
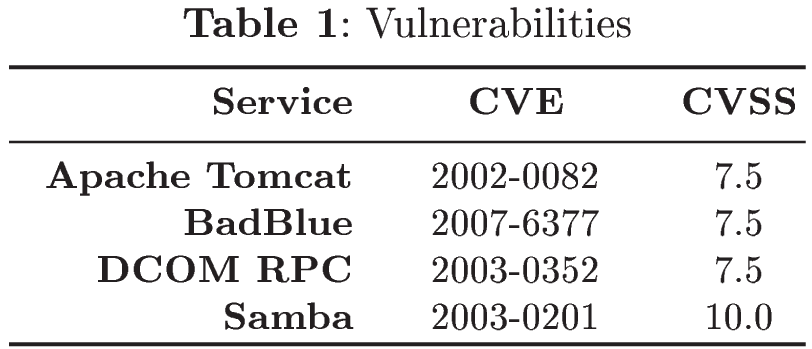
The ASNM-TUN dataset (Advanced Security Network Metrics & Tunneling Obfuscations) consists of ASNM features [1, 2] extracted from tcpdump capture of obfuscated malicious and legitimate TCP communications on selected vulnerable network services (Table 1). The selection of vulnerable services was aimed on high severity of their successful exploitation utilizing buffer overflow vulnerabilities, which leaded to remote shell code execution through established backdoor communication. We employed tunneling of malicious traffic in HTTP and HTTPS protocols as obfuscation techniques when exploiting vulnerable services in virtual network conditions. For the purpose of simulating real network conditions, we executed each malicious and legitimate network communication four times in four different network traffic modifications. Network traffic modifications differ in the alteration degree of the traffic and are divided into four categories:
The first category represents reference output without any modification to configuration. All experiments ran on the same host machine to minimize deviations among different tests.
The second category is dedicated to simulate traffic shaping. Therefore, all packets were forwarded with higher time delays. For this purpose, the special gateway machine with limited processor's performance was used. This machine was also fully loaded to emulate slower packets processing than in the first scenario.
The third category is supposed to simulate traffic policing when some of packets were dropped during the processing on the network gateway node. In this case, a custom packet dropper was used on the gateway node and 25% of packets were dropped, resulting in output which contains re-transmitted packets.
The fourth category represents transmission on an unreliable network channel, thus 25% of packets were corrupted during processing on the network gateway node.
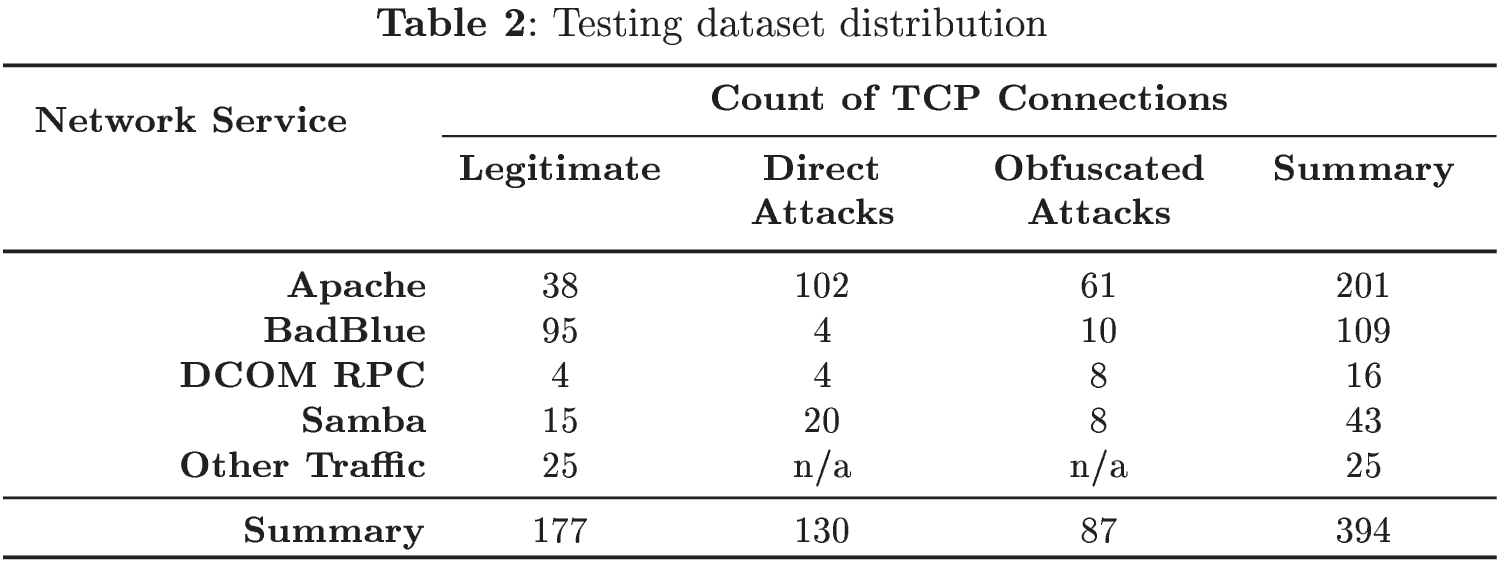
Legitimate representatives of the dataset was collected from two sources. The first source represented legitimate traffic simulation in our virtual network architecture and also employed network traffic modifications for the purpose of real network simulation. As the second source, common usage of all selected services was captured in campus network, and all traffic was anonymized and further filtered on high severity alerts by signature based NIDS Suricata and SNORT through Virus Total API. Note that SNORT was equipped with Sourcefire VRT ruleset and SURICATA utilized Emerging Threats ETPro ruleset. The final composition of the dataset is depicted in Table 2.
Labeling
The ASNM-TUN dataset contains 4 types of labels which are enumerated by increasing order of their granularities in the following listing:
The two-class label, denoted as label_2, says whether an actual record represents network attack or not.
The three-class label, denoted as label_3, distinguishes among legitimate traffic (symbol 3), direct and obfuscated network attacks (symbols 1 and 2).
The third label, denoted as label_poly, is composed of 2 parts: a) three-class label, and b) acronym of network service. The label represents type of communication on particular network service.
The last label, denoted as label_poly_s, is composed of 3 parts: a) three-class label, b) acronym of network service, and c) employed network modification technique. The label has almost the same interpretation as the previous one, but moreover introduces employed network modification technique (identified by letter from listing).
Introducing Paper
ASNM-TUN dataset in its actual version does not have introducing paper, however it was first time utilized in dissertation thesis [2]. Note that previous version of this dataset, which had not legitimate traffic filtered by SNORT and SURICATA, was introduced and used in papers [3] and [4]. The unfiltered/unofficial version of the dataset is available [here], but is not recommended to use and serves only for reproducing the results of the experiments.
Download
ASNM-TUN dataset in CSV format can be downloaded [here].
References
-
HOMOLIAK Ivan, BARABAS Maros, CHMELAR Petr, DROZD Michal a HANACEK Petr.: ASNM: Advanced Security Network Metrics for Attack Vector Description. In: Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Security & Management. Las Vegas: Computer Science Research, Education, and Applications Press, 2013, s. 350-358. ISBN 1-60132-259-3. Download link.
-
HOMOLIAK Ivan.: Intrusion Detection in Network Traffic. Dissertation thesis, University of Technology Brno, Faculty of Information Technology, 2016. Download link.
-
HOMOLIAK Ivan, OVSONKA Daniel, GREGR Matej a HANACEK Petr. NBA of Obfuscated Network Vulnerabilities' Exploitation Hidden into HTTPS Traffic. In: Proceedings of International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST-2014). London: IEEE Computer Society, 2014, s. 311-318. ISBN 978-1-908320-40-7. Download link.
-
HOMOLIAK Ivan, OVSONKA Daniel, KORANDA Karel a HANACEK Petr. Characteristics of Buffer Overflow Attacks Tunneled in HTTP Traffic. In: International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology. Roma: IEEE Computer Society, 2014, s. 188-193. ISBN 978-1-4799-3531-4. Download link.

